| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 최소공배수
- 조합
- HashMap
- 메뉴리뉴얼
- 영문자 확인
- fragment identifier
- python
- dfs
- 동적계획법
- pandas
- 문자열
- Java
- 완전탐색
- 완전 탐색
- 2017 카카오 코드
- 순열
- Stack
- 알고리즘
- 후위 표기법
- 에라토스테네스의 체
- 튜플
- 어려웠던 문제
- 보이어무어
- 규칙찾기
- 점프와 순간이동
- Dynamic Programming
- 반복문
- HashSet
- 쿼드압축 후 개수세기
- 프로그래머스
- Today
- Total
csmoon1010의 SW 블로그
Queue(큐) 자료구조 본문
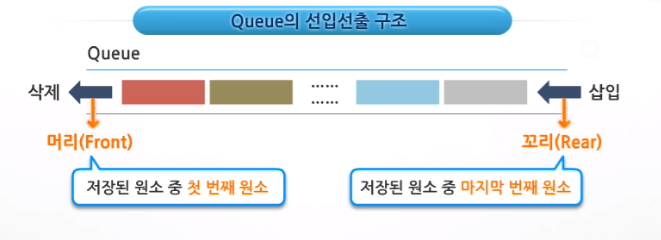
1. 특성
- 선입선출구조(FIFO : First In First Out) : 먼저 삽입된 원소가 먼저 삭제
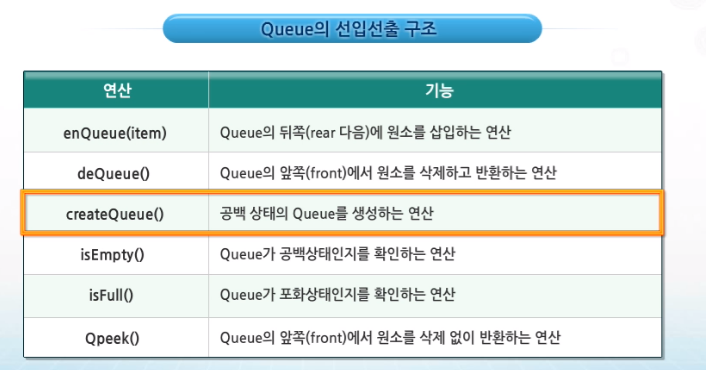
2. 주요 연산
3. 유형
(1) 선형 큐
- 1차원 배열 사용 (큐의 크기 == 배열 크기)
- 상태 표현 :
- 초기 front = rear = -1
- 공백 front == rear
- 포화 rear == n-1
- 문제점 : 앞부분에 활용 공간이 있음에도 불구하고 포화 상태로 인식하여 삽입 불가능
- 대안
① 매 연산이 이루어질 때마다 저장된 원소들을 배열 앞부분으로 모두 이동
BUT 낮은 효율성(이동에 많은 시간 소요)
② 원형 큐 사용
- 코드 ( enQueue, deQueue, isEmpty, isFull, qPeek )
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LinearQueue {
static int size = 5;
static int front = -1;
static int rear = -1;
static int[] queue;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
queue = new int[size];
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String[] order = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
if (order.length == 2 && order[0].equals("add")) {
enQueue(Integer.parseInt(order[1]));
} else if (order[0].equals("poll")) {
deQueue();
} else if (order[0].equals("peek")) {
qPeek();
} else {
System.out.println("finish");
break;
}
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty() {
boolean answer = false;
if (front == rear) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static boolean isFull() {
boolean answer = false;
if (rear == size-1) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static void enQueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Full");
} else {
queue[++rear] = item;
System.out.println(item + " is added to Queue");
}
}
public static void deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
int peek = queue[++front];
System.out.println(peek + " is deleted from Queue");
}
}
public static void qPeek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
System.out.println(queue[front+1]);
}
}
}
(2) 원형 큐
- 1차원 배열 사용 + 논리 (배열의 처음과 끝이 연결되는 원형 형태)
- 상태 표현
초기 front = rear = 0
front가 있는 자리는 사용하지 않고 빈자리로 둠

public static boolean isEmpty() {
boolean answer = false;
if (front == rear) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static boolean isFull() {
boolean answer = false;
if (front == (rear+1)%size) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static void enQueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Full");
} else {
rear = (rear+1)%size;
queue[rear] = item;
System.out.println(item + " is added to Queue");
}
}
public static void deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
front = (front+1)%size;
int peek = queue[front];
System.out.println(peek + " is deleted from Queue");
}
}
public static void qPeek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
System.out.println(queue[(front+1)%size]);
}
}
(3) 연결 큐
- Linked List를 이용 (노드들이 링크로 연결되어 있음)
- 상태 표현
초기/공백 front = rear = NULL
포화 상태 X
import java.util.Scanner;
class Node { //LinkedQueue의 요소인 Node class
int value;
Node next;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
public class LinkedQueue {
static Node front = null;
static Node rear = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String[] order = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
if (order.length == 2 && order[0].equals("add")) {
enQueue(Integer.parseInt(order[1]));
} else if (order[0].equals("poll")) {
deQueue();
} else if (order[0].equals("peek")) {
qPeek();
} else {
System.out.println("finish");
break;
}
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty() {
boolean answer = false;
if(front == null) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static void enQueue(int item) {
Node node = new Node(item);
if(isEmpty()) {
front = node;
} else {
rear.setNext(node);
}
rear = node;
System.out.println(item + " is added to Queue");
}
public static void deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
int peek = front.value;
Node previous = front;
front = previous.next; //front를 다음 Node로 조정
previous.next = null;
if(isEmpty()) { //노드가 없는 경우 rear도 조정해줘야 한다!
rear = null;
}
System.out.println(peek + " is deleted from Queue");
}
}
public static void qPeek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
System.out.println(front.value);
}
}
}
(4) 우선순위 큐
: 우선순위를 가진 항목들을 저장하는 큐
높은 우선순위 --> 같다면 선입선출
- 활용 : 시뮬레이션 시스템, 네트워크 트래픽 제어, 운영체제 task scheduling
- 자료구조
① 배열 활용 : 우선순위 별 배열 구현
(문제점) : 삽입, 삭제 시 원소의 재배치 --> 소요 시간, 메모리 낭비 큼
② 연결 리스트 활용
import java.util.Scanner;
class PNode { //LinkedQueue의 요소인 Node class
int value;
PNode previous;
PNode next;
PNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.previous = null;
this.next = null;
}
public void setLink(PNode previous, PNode next) {
this.previous = previous;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class PriorityQueue {
static PNode front = null;
static PNode rear = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String[] order = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
if (order.length == 2 && order[0].equals("add")) {
enQueue(Integer.parseInt(order[1]));
} else if (order[0].equals("poll")) {
deQueue();
} else if (order[0].equals("peek")) {
qPeek();
} else if (order[0].equals("all")) {
printQueue();
} else {
System.out.println("finish");
break;
}
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty() {
boolean answer = false;
if(front == null) {
answer = true;
}
return answer;
}
public static void enQueue(int item) { //priority : 값이 클수록 높은 우선순위
PNode node = new PNode(item);
if(isEmpty()) {
front = node;
rear = node;
} else {
PNode current = rear;
while(current != front && current.value < node.value) {
current = current.previous;
}
if(current == front && current.value <= node.value) { //front에 위치해야 하는 경우
front.setLink(node, front.next);
node.setLink(null, front);
front = node;
} else if(current == rear && current.value >= node.value) { //rear에 위치해야 하는 경우
rear.setLink(rear.previous, node);
node.setLink(rear, null);
rear = node;
} else { //중간에 위치해야 하는 경우
PNode oldNext = current.next;
oldNext.setLink(node, oldNext.next);
current.setLink(current.previous, node);
node.setLink(current, oldNext);
}
}
System.out.println(item + " is added to Queue");
}
public static void deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
int peek = front.value;
PNode previous = front;
front = previous.next; //front를 다음 Node로 조정
previous.next = null;
if(isEmpty()) { //노드가 없는 경우 rear도 조정해줘야 한다!
rear = null;
}
System.out.println(peek + " is deleted from Queue");
}
}
public static void qPeek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
} else {
System.out.println(front.value);
}
}
public static void printQueue() {
PNode current = front;
while(current != null) {
System.out.print(current.value + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
③ 힙 자료구조 활용
4. 자바에서의 큐
2020/04/16 - [Programming Language/Java] - 자바 API 클래스 정리 & 컬렉션 프레임워크
(1) LinkedList
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String[] order = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
if (order.length == 2 && order[0].equals("add")) {
q.add(order[1]);
} else if (order[0].equals("poll")) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
} else if (order[0].equals("peek")) {
System.out.println(q.peek());
} else if (order[0].equals("all")) {
for(String s : q) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
} else {
System.out.println("finish");
break;
}
}
}
}
(2) PirorityQueue
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Student{
String name;
int grade;
public Student(String name, int grade) {
this.name = name;
this.grade = grade;
}
}
public class JavaQueue2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparator<Student> comp = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.grade - s2.grade;
}
};
PriorityQueue<Student> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(comp);
Student s1 = new Student("mhj", 90);
Student s2 = new Student("kdy", 100);
Student s3 = new Student("hrj", 50);
Student s4 = new Student("mark", 70);
pq.add(s1);
pq.add(s2);
pq.add(s3);
pq.add(s4);
for(Student s : pq) {
System.out.println(s.name + " " + s.grade);
}
}
}
Comparator 클래스를 함께 써 세부적인 우선순위 설정 가능
(출처)
'Coding Test > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| List 자료구조 (0) | 2021.02.14 |
|---|---|
| 백트래킹 기법(Backtracking) (0) | 2021.01.04 |
| Stack(스택) (0) | 2020.12.20 |
| 패턴 매칭 알고리즘(Brute Force, KMP, 보이어 무어) (0) | 2020.11.29 |
| Search(검색, 탐색) _ Sequential Search, Binary Search (0) | 2020.11.17 |



