| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Stack
- 반복문
- 문자열
- pandas
- 최소공배수
- 프로그래머스
- 완전 탐색
- Dynamic Programming
- 알고리즘
- 2017 카카오 코드
- 규칙찾기
- 완전탐색
- 후위 표기법
- 어려웠던 문제
- 순열
- 쿼드압축 후 개수세기
- 메뉴리뉴얼
- python
- HashMap
- dfs
- 동적계획법
- 에라토스테네스의 체
- Java
- HashSet
- 영문자 확인
- 보이어무어
- 튜플
- 조합
- 점프와 순간이동
- fragment identifier
- Today
- Total
csmoon1010의 SW 블로그
[201106] 수식 최대화 - 2020 카카오 인턴십(level2) 본문
0. 문제 유형 : 순열(완전 탐색, DFS), 적절한 자료구조 선택
1. 문제 이해
programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/67257
코딩테스트 연습 - 수식 최대화
IT 벤처 회사를 운영하고 있는 라이언은 매년 사내 해커톤 대회를 개최하여 우승자에게 상금을 지급하고 있습니다. 이번 대회에서는 우승자에게 지급되는 상금을 이전 대회와는 다르게 다음과
programmers.co.kr
(1) 주요 요구사항
- 수식(String expression) : 숫자들과 3가지의 연산문자(+, -, *)로 이루어진 수식
- 연산자 : 기존과 다르게 연산자의 우선순위를 새로 정의
- 출력 : 만들 수 있는 연산자의 우선순위들에 따라 수식을 연산한 결과 절댓값의 최대값
(2) 추가 조건
- 연산자 우선 순위
① 같은 순위는 없어야 됨 (ex> + > - > * )
② 수식에는 1개 이상의 연산자가 포함 == 무조건 3개의 연산자인 것은 아님 == 연산자가 없는 경우는 존재X
- 피연산자의 범위
: 각 피연산자의 범위는 0이상 999이하 BUT 최종결괏값 범위는 2^63 -1 이하
→ int 범위를 넘어갈 수 있으므로 전부 long으로 계산하기
2. 전략
(1) 주어진 expression의 전처리(숫자, 연산자 구분 / 연산자 종류 파악)
- 숫자, 연산자 구분 : Character의 isDigit()이용 / 숫자는 다음 연산자or문자열 끝이 나올 때까지 임시스트링에 저장
→ ArrayList<String> expr에 저장
- 연산자 종류 파악 : (2)의 연산자 우선순위의 결정을 위해 수식에 포함된 연산자 종류를 파악할 필요
→ 연산자 발견 시 HashSet<Character>에 저장
(2) 연산자의 우선 순위 경우의 수
: "순열" 알고리즘 활용
① 방법 1 swap : 배치할 index를 정하고 뒤의 요소들과 swap하면서 경우의 수 만들기
② 방법 2 visited : 매 시행마다 원소의 visited 여부 확인 ( 더 간단하지만 true인 경우까지 다시 살펴보기 위해 반복문)
→ 문제 풀이의 다양한 시도를 위해 visited 방법 이용
(3) 각 우선 순위에 맞게 연산 진행
: 가장 높은 우선순위이면 바로 연산, 낮은 우선순위이면 연산을 미루는 방식
→ 적절한 자료구조의 선택과 연산 수행 조건을 오류 없이 세우는 것이 중요
① 방법 1 : ArrayList<String>만 사용, 해당 연산자를 만나자마자 연산
- input : ArrayList<String> 연산의 대상이 되는 수식
- output : ArrayList<String> 우선순위에 맞는 연산을 위해 사용하는 자료구조. Stack 역할을 위해 top변수 관리
- 프로세스
[재귀 알고리즘]
- 모든 연산이 완료될 때까지 아래 과정을 반복한다.
- 높은 우선순위의 연산자부터 차례대로 연산 대상이 된다.
[조건]
- target 연산자인 경우 : output의 top에 있는 수와 input의 다음 수를 바로 연산 → output의 top에 대체(set)
- 그 외 : output에 add 후 top을 증가
② 방법 2: Stack<String>도 이용, 해당 연산자는 stack에 저장한 후 숫자를 만났을 때 stack의 peek에 위치하면 연산
- input : ArrayList<String> 연산의 대상이 되는 수식
※ output의 결과가 나중에 input으로 들어가야 됨
→ Collections들은 new ArrayList(컬렉션변수)를 통해 쉽게 ArrayList로 변경이 가능하다.
- output : Stack<String> 우선순위에 맞는 연산을 한 결과. peek, pop을 통해 가장 최근에 추가된 원소에 쉽게 접근 가능
- 프로세스
[재귀 알고리즘]
- 모든 연산이 완료될 때까지 아래 과정을 반복한다.
- 높은 우선순위의 연산자부터 차례대로 연산 대상이 된다.
[조건]
- 숫자이면서 빈 stack이 아닌 경우
만약 stack의 peek이 대상 연산자이면 두 번의 pop()을 진행
1st pop() : 해당 연산자 , 2nd pop() : 연산을 수행할 다른 피연산자
2nd pop()과 함께 연산을 수행한 후 push()를 통해 다시 stack에 저장한다.
stack의 peek이 다른 연산자이면 그대로 push()만 진행
- 연산자 : stack에 push()
++ 연산자의 확인, 연산 수행을 위한 함수 isOperator, calculate 구현
3. 참고사항
(1) expression의 전처리
① 나의 풀이에서는 연산자와 피연산자를 분리할 필요가 없었지만, 둘을 분리해서 푸는 알고리즘도 존재 가능
String클래스의 split과 regex 표현을 통해 숫자만 분리시킬 수 있다.
String[] a = expression.split("[+, \\-, *]");② String 클래스의 contains : 각 연산자의 포함 여부를 확인할 수 있음
if(expression.contains("+")) expr.add("+");
(2) 연산 : 정해진 우선순위에 따라 후위표기법으로 바꾼 뒤 연산 진행
① 후위 표기법으로 바꾸기
1. 피연산자 : 그대로 출력
2. 연산자
(1) 스택이 비었음 : 스택에 push
(2) 스택에 연산자 존재 : 우선순위 비교
스택 >= 현재 : 우선순위 높은 연산자 모두 pop, 현재 연산자 push
스택 < 현재 : 현재 연산자 push
3. 괄호
(1) 오른쪽 괄호 ')' : top에 왼쪽 괄호 '('가 올 때까지 연산자 pop
(2) 왼쪽 괄호 '(' : 무조건 push/가장 낮은 우선순위
▶ 더 이상 없으면 스택이 빌 때까지 pop
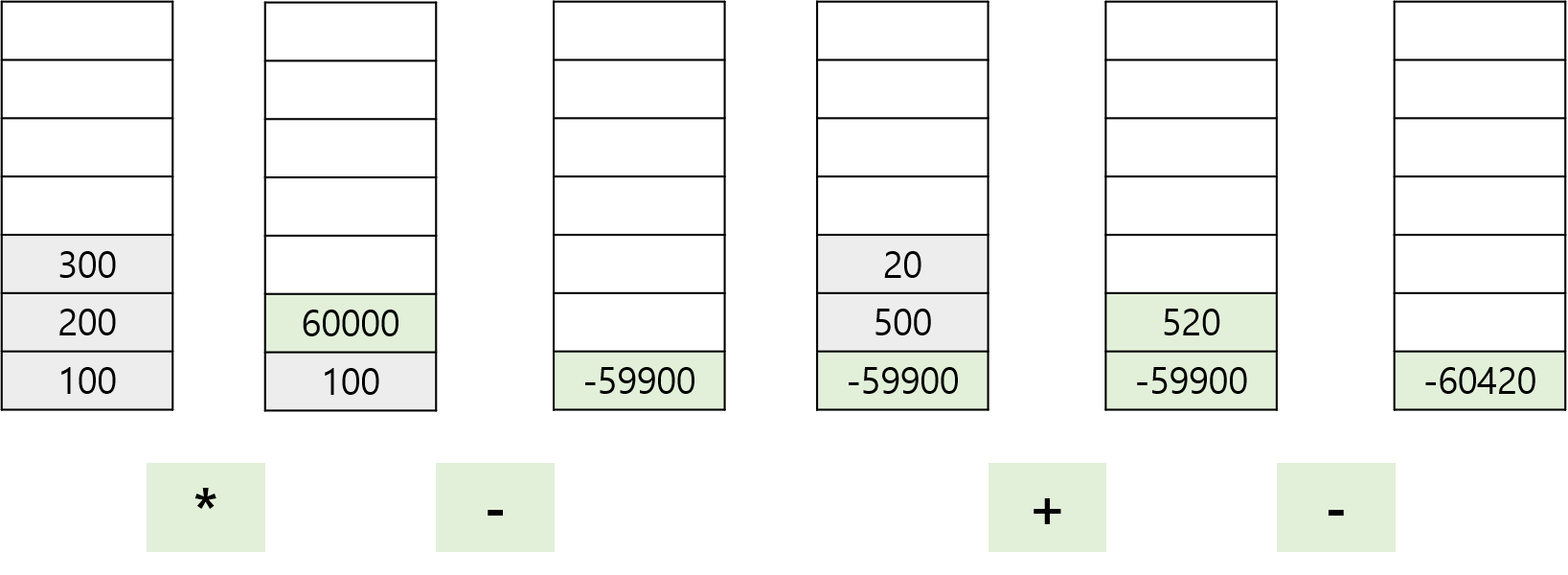
ex> "100-200*300-500+20" * > + > -
후위 표기법 : 100 200 300 * - 500 20 + -
② 후위 표기법의 계산
1. 피연산자 : 스택에 push
2. 연산자 : 두 개의 수 pop하여 계산하고 다시 stack에 push(아래있는 수가 먼저 위치)
▶ 더 이상 없으면 스택에서 마지막 값 pop = 연산의 결과
4. 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static String[][] allCase;
static int index;
public long solution(String expression) {
long answer = 0;
//1.우선 순위 배열 정하기
//연산자 종류 파악
ArrayList<String> expr = new ArrayList<>();
HashSet<Character> operators = new HashSet<>();
String numString = "";
for(int i = 0; i < expression.length(); i++){
char c = expression.charAt(i);
if(!Character.isDigit(c)){
operators.add(c); //**Character.isDigit
expr.add(numString); numString = "";
expr.add(Character.toString(c));
}
else{
numString += Character.toString(c);
if(i == expression.length()-1) expr.add(numString);
}
}
//팩토리얼 - 모든 경우의 수(순열도 있음)
int n = operators.size(); int size = 1; int o = 0;
char[] variety = new char[n];
for(char c : operators) variety[o++] = c;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) size*= i;
allCase = new String[size][n];
index = 0;
perm(variety, n, n, 0, "", new boolean[n]);
//2. 연산 수행
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
String[] priority = allCase[i];
answer = Math.max(answer, Math.abs(calcExp2(expr, priority, 0)));
}
return answer;
}
public void perm(char[] a, int n, int k, int level, String s, boolean[] v){//visited
if(level == k){
allCase[index++] = s.split("");
}else{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(!v[i]){
v[i] = true;
perm(a, n, k, level+1, s + Character.toString(a[i]), v);
v[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
//ArrayList만 이용한 경우 & priority check를 연산일 때
public long calcExp(ArrayList<String> input, String[] priority, int level){
if(level == priority.length) //연산 완료
return Long.parseLong(input.get(0));
else{
ArrayList<String> output = new ArrayList<>(); int top = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < input.size(); i++){
if(isOperator(input.get(i), priority)){ //target 연산자
if((input.get(i)).equals(priority[level])){
long a = Long.parseLong(output.get(top));
long b = Long.parseLong(input.get(++i));
output.set(top, Long.toString(calculate(a, b, priority[level])));
}else{ //다른 연산자
output.add(input.get(i)); top++;
}
}else{ //숫자
output.add(input.get(i)); top++;
}
}
return calcExp(output, priority, level+1);
}
}
//Stack 이용한 경우 & priority check를 숫자일 때(stack의 pop을 이용할 수 있으므로)
public long calcExp2(ArrayList<String> input, String[] priority, int level){
if(input.size() == 1) return Long.parseLong(input.get(0));
else{
Stack<String> output = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < input.size(); i++){
if(!isOperator(input.get(i), priority) && !output.empty()){
if((output.peek()).equals(priority[level])){
output.pop();
long a = Long.parseLong(output.pop());
long b = Long.parseLong(input.get(i));
output.push(Long.toString(calculate(a, b, priority[level])));
}else output.push(input.get(i));
}else output.push(input.get(i));
}
return calcExp2(new ArrayList(output), priority, level+1);
}
}
public boolean isOperator(String s, String[] priority){
boolean result = false;
for(String p : priority){
if(s.equals(p)){
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public long calculate(long a, long b, String op){
long answer = 0;
if(op.equals("+")) answer = a+b;
else if(op.equals("-")) answer = a-b;
else answer = a*b;
return answer;
}
}'Coding Test > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [201107] 짝지어 제거하기 - 2017 팁스타운(level2) (0) | 2020.11.10 |
|---|---|
| [201106] 쿼드압축 후 개수 세기 - 월간 코드 챌린지 시즌1(level2) (0) | 2020.11.06 |
| [201105] 삼각 달팽이 - 월간 코드 챌린지 시즌1(level2) (0) | 2020.11.05 |
| [201105] 두 개 뽑아서 더하기 - 월간 코드 챌린지 시즌1(level1) (0) | 2020.11.05 |
| [201027] 튜플 - 2019 카카오 개발자 겨울 인턴십(level2) (0) | 2020.10.28 |


